What is Malt?
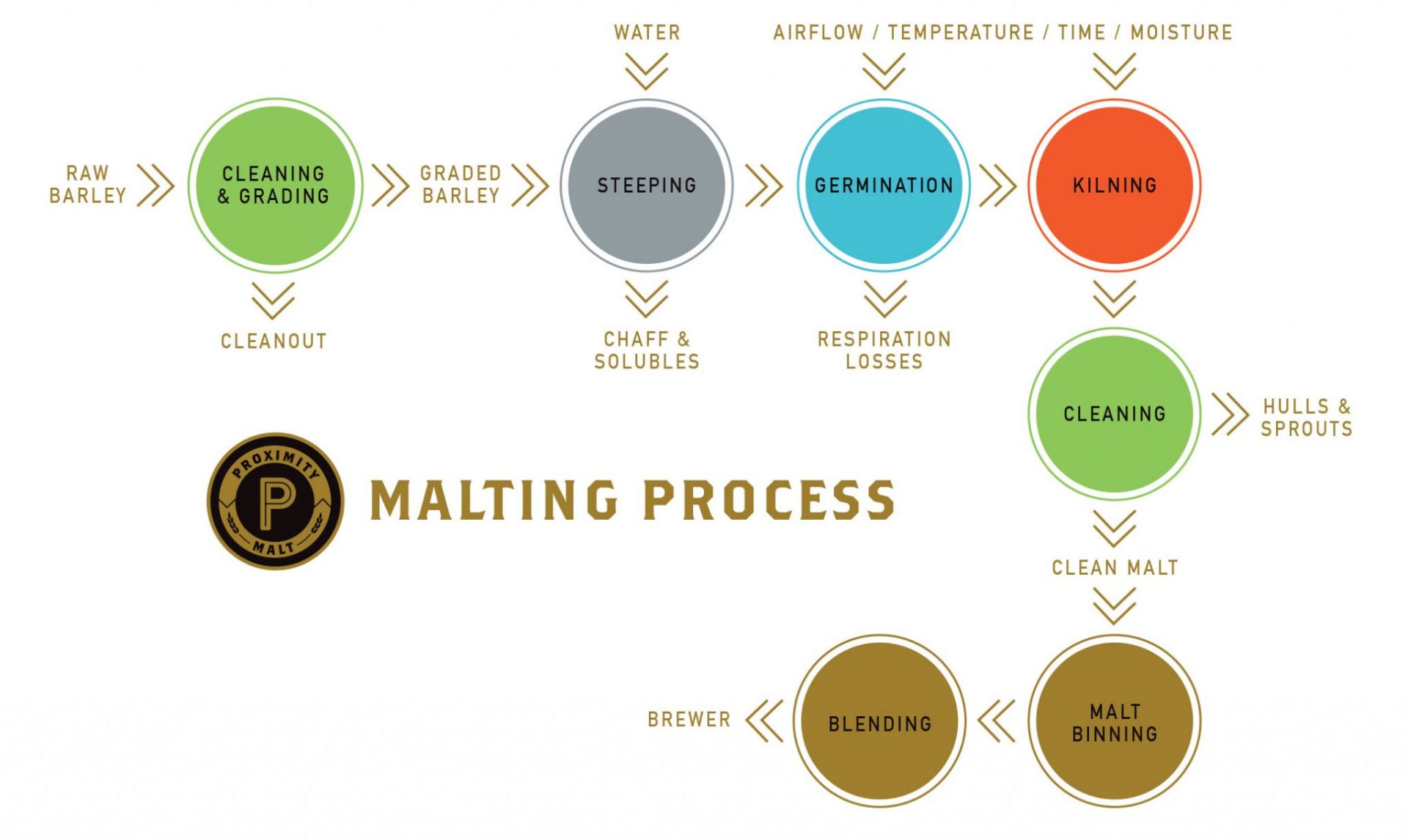
Cereal grains such as barley are malted in order to convert each kernel’s starch to fermentable sugars, and then to stabilize it at a low moisture level, so that it can be used by brewers and distillers to convert those sugars to ethanol. Three steps comprise the heart of the malt process: Steeping. Germination. Kilning. Once the grain is purchased, received, and foreign material is removed, then the process can begin:
Steeping
Cleaned barley is submerged in aerated water to activate the embryo, releasing hormones that initiate enzymatic development. Rootlets begin to grow. The grain’s moisture increases from about 12% to 40-45%, ensuring full hydration of the starchy endosperm.
Germination
Hydrated, chitted barley transfers to germination beds, and continues to grow for approximately 4 days. The kernels ‘modify,’ meaning the complex proteins surrounding starches break down, opening up starch reserves.
Kilning
Increasing temperature and decreasing moisture dries the grain and stops germination. In kilning, the controlled time, temperature and moisture protocol preserves enzymes that are necessary for brewing. The two primary steps of kilning are called ‘withering’ and ‘curing.’ Maillard reactions develop malty flavors. Finally, the finished malt is polished, or ‘de-culmed’ to remove chits and rootlets, and is stored at the malthouse.
PROXIMITY MALT – MALTING TECHNOLOGY
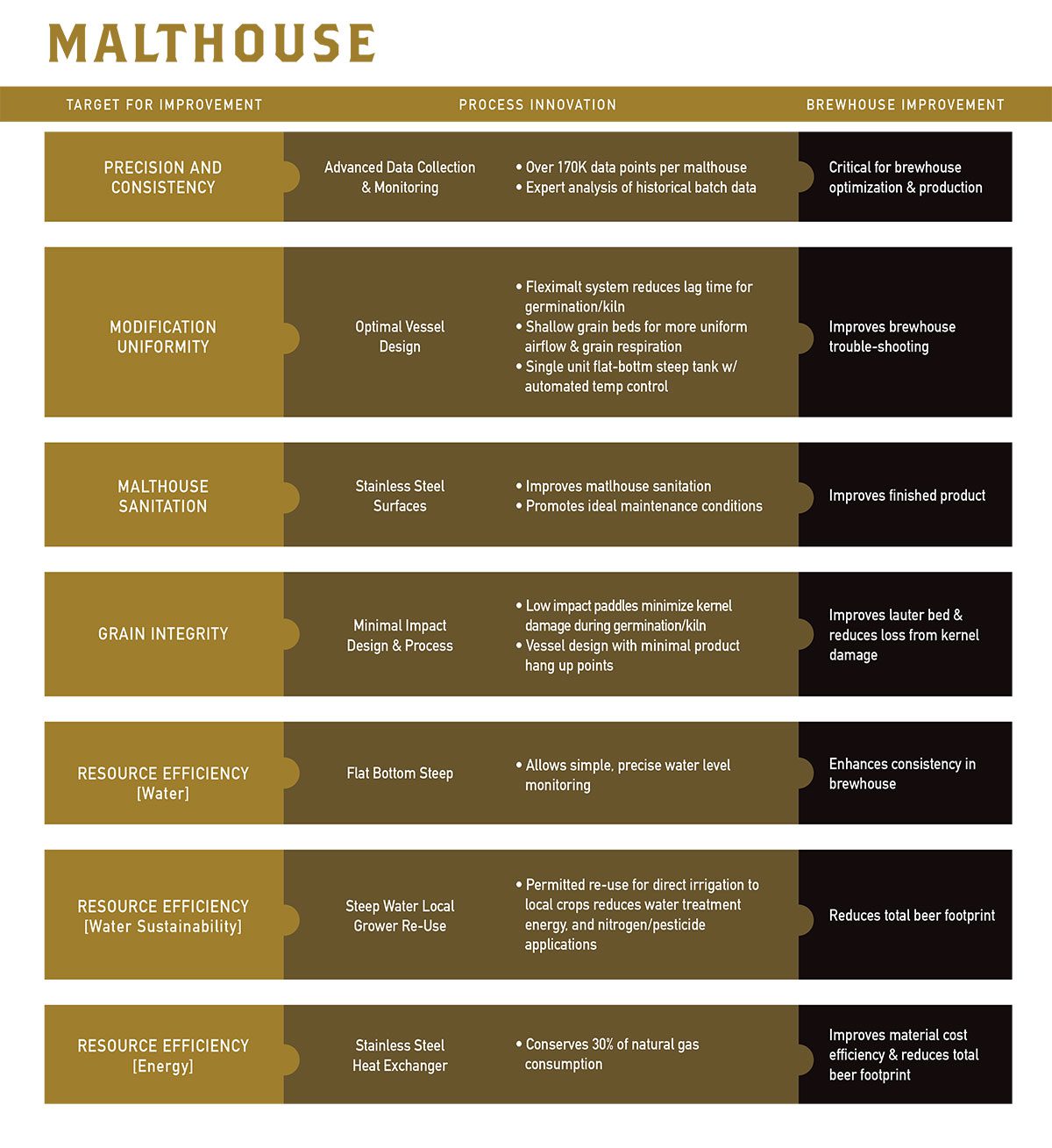
Purpose-built to serve craft brewing and distilling and food users, Proximity Malt’s facilities improve the traditional malt process. Our team of industry veterans designed smart adaptations of new technology and process advancements-beginning with precise process control and data collection. Our customers experience better performance due to the malt’s improved consistency, modification uniformity, sanitation,grain integrity and precise adherence to specifications, within the parameters of the raw material: